Exploring the Function of a Geotechnical Engineer Description and Duties
Exploring the Function of a Geotechnical Engineer Description and Duties
Blog Article
The Value of Geotechnical Design in Resolving Environmental Difficulties and Enhancing Building Safety And Security
Geotechnical engineering offers as a keystone in the intersection of environmental stewardship and construction safety and security, giving crucial understandings into the behavior of soil and rock under different problems. This technique not just addresses pushing environmental challenges such as dirt disintegration and groundwater security yet additionally enhances the toughness of facilities versus all-natural hazards. By carrying out strategic site investigations and tailored mitigation steps, geotechnical designers play an important role in protecting both human lives and ecological integrity. The intricacies of these challenges raise vital questions regarding the future direction of this field and its effects for sustainable growth.

Function of Geotechnical Design
Geotechnical engineering plays a critical duty in the style and building and construction of facilities by attending to the actions of dirt and rock products under numerous problems. This area of design is vital for comprehending the interaction in between frameworks and the ground, which includes figuring out the load-bearing capacity of soil, assessing stability, and forecasting potential negotiation or failure.
Geotechnical engineers are in charge of carrying out website examinations, which involve sampling and testing dirt and rock to collect data on their chemical and physical residential or commercial properties. This info is important for designing foundations, preserving walls, and other earth-retaining structures that ensure safety and longevity. Geotechnical design educates the choice of ideal construction techniques and materials, therefore reducing threats associated with dirt actions.
Furthermore, the combination of geotechnical engineering principles into city planning and ecological administration is important for attending to obstacles such as ground contamination and groundwater monitoring. By recognizing geotechnical factors, designers can develop sustainable remedies that improve the durability of facilities against natural dangers, while likewise promoting ecological stewardship. Eventually, the role of geotechnical engineering is crucial for accomplishing secure, long lasting, and ecologically mindful building and construction methods.
Dirt Disintegration Mitigation
Soil erosion postures a considerable threat to both ecological stability and infrastructure integrity, impacting approximately 24 billion lots of abundant soil lost every year worldwide. This phenomenon is worsened by elements such as deforestation, urbanization, and inadequate agricultural practices. Geotechnical design plays a critical function in developing effective dirt disintegration reduction strategies that secure both the atmosphere and building and construction tasks.
One method entails the application of erosion control methods such as plant life planting, which stabilizes soil through origin systems. Additionally, the building of maintaining walls and balconies can properly decrease surface drainage and secure vulnerable locations from disintegration. Proper water drainage layout is also critical; it minimizes water accumulation and guides excess overflow away from critical frameworks.
Additionally, geotechnical engineers use soil stablizing techniques, such as the application of geotextiles and biodegradable floor coverings, to improve soil cohesion and protect against deterioration - geotechnical engineer description. Regular monitoring and analysis of erosion-prone sites make it possible for timely treatments, making sure long-term sustainability. By integrating these approaches, geotechnical engineering not only mitigates the influences of soil erosion but likewise adds to the strength of infrastructure versus environmental obstacles, ultimately promoting a more secure and a lot more lasting built environment
Groundwater Defense Techniques
Groundwater works as a crucial resource for alcohol consumption water, farming, and commercial processes, making its security essential for look at this site ecological sustainability and public health. Efficient groundwater security techniques are vital in alleviating contamination risks and ensuring the longevity of this source.
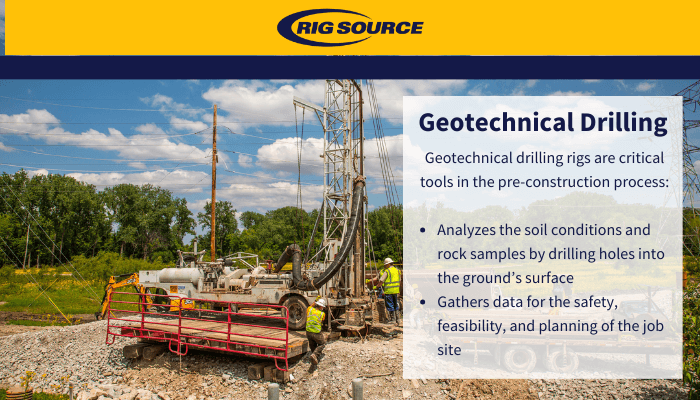
Regular monitoring of groundwater high quality is additionally important, making it possible for very early detection of contamination resources and assisting in timely removal initiatives. Using sophisticated innovations, such as geophysical surveys and remote picking up, help in determining possible risks to groundwater gets.
Furthermore, public education and stakeholder involvement are vital, cultivating area support for groundwater security campaigns. geotechnical specialist. By integrating governing procedures, technological developments, and community involvement, we can produce an extensive framework that safeguards groundwater sources while promoting lasting development and building practices
Landslide Risk Administration
Landslides pose substantial risks to both human security and framework, making effective threat management methods vital. Geotechnical engineering plays a critical function in determining, assessing, and mitigating landslide risks. An extensive understanding of slope stability, soil auto mechanics, and hydrology is important for creating reliable threat administration strategies.
The very first step in landslide threat management entails detailed website examinations, that include geological mapping and dirt testing. These examinations help engineers assess the possibility for landslides by recognizing important factors such as slope angles, soil make-up, and water content. Using sophisticated modern technologies such as remote sensing and geophysical surveys can boost the accuracy of these evaluations.
When risks are determined, proper reduction measures can be carried out. These may include engineering services such as retaining wall surfaces, water drainage systems, and slope stablizing strategies. Checking systems should be established to discover indications of ground movement and changes in water degrees, allowing for proactive interventions.

Enhancing Construction Security
Building and construction websites frequently provide a myriad of visit this website dangers that can jeopardize worker security and job integrity. Geotechnical design plays an essential role in enhancing construction safety and security by offering necessary understandings right into subsurface conditions. Via thorough dirt and rock evaluation, geotechnical engineers can recognize potential dangers, such as soil instability, groundwater issues, and seismic susceptabilities, which may jeopardize the security of building and construction tasks.
Carrying out geotechnical options, such as appropriate structure style and the usage of maintaining structures, mitigates these dangers considerably. These services not only make certain the stability of the structures being developed yet likewise develop a more secure working atmosphere for construction workers.
Furthermore, promoting a culture of security through training and adherence to developed security methods even more enhances imp source building website security. By integrating geotechnical experience into the planning and execution phases, building and construction jobs can achieve higher safety and security standards, ultimately shielding workers and guaranteeing effective project completion.
Conclusion
Finally, geotechnical design functions as an essential discipline in tackling environmental obstacles and promoting building and construction security. Through efficient soil erosion reduction, groundwater protection approaches, and landslide danger monitoring, geotechnical engineers add to the development of resilient framework. The integration of these practices cultivates a much safer building and construction environment and boosts the sustainability of civil design tasks. Inevitably, the proficiency of geotechnical designers is crucial in guarding both natural deposits and human lives versus prospective risks.
Geotechnical design serves as a foundation in the intersection of environmental stewardship and building safety, supplying crucial understandings into the habits of soil and rock under different problems. Geotechnical engineering notifies the choice of appropriate building techniques and products, consequently minimizing risks linked with dirt behavior.
Geotechnical engineering plays an essential duty in developing effective soil erosion mitigation techniques that protect both the setting and construction projects.
Furthermore, geotechnical engineers utilize dirt stablizing techniques, such as the application of geotextiles and naturally degradable floor coverings, to improve soil communication and avoid deterioration. Through thorough soil and rock evaluation, geotechnical designers can identify potential risks, such as dirt instability, groundwater concerns, and seismic susceptabilities, which might jeopardize the safety of construction activities.
Report this page